Blog #132 – Who was the better democrat – Jefferson or Jackson?
What I am asking you to do with this blog is something that historians typically engage in – a comparison / contrast between two important figures pertaining to an agreed-upon set of standards. In this case, we will be comparing the presidencies of Thomas Jefferson and Andrew Jackson to see who was the better democrat (small d, not the Democratic Party, though both are seen as the forefathers of today’s modern party) and promoted democratic policies and ideas during their time in office. As for democratic principles, we should work from the following list:
- Who promoted political involvement for the average person, for instance, the expansion of the right to vote? How was this done?
- Who was considered for political office? Who chose the presidential candidates during their time?
- How did each man view the federal government’s role in promoting the economy?
- How did each man view the relationship between the federal and state governments? Did they exercise limited power as the executive?
The Common Man and Political Involvement
Jefferson believed in an agrarian vision for America. Remember the notes on Jeffersonian agrarianism – we saw that he believed that independent yeoman farmers who had easy access to abundant farmland would provide the bedrock of American democracy. These farmers owned their land outright and that land provided the basis on which they could vote in all manner of elections (though in many states, the average voters did NOT choose the electors of the Electoral College). During Jefferson’s presidency, Jefferson purchased the Louisiana Territory in 1803 which, when settled, would allow for new generations of American farmers to establish their own farms and be able to vote. Also, to Jefferson, education was important for these farmers to stay informed on political topics, and so he promoted public schools while governor of Virginia and president. However, during his time, political parties only functioned at the national level. Lastly, unlike the Federalists, Jefferson trusted the common man to make the right decisions politically and didn’t view them as an unruly mob incapable of making rational decisions.
Before and during Jackson’s presidency, suffrage, or the right to vote, expanded as new western states eliminated property requirements to vote and eastern states began to modify their state constitutions to allow for more urban workers and landless white men to vote. For some African American men, their voting rights were taken away or a very high bar for property requirements were demanded like in New York in 1821 or outright took away their vote in Pennsylvania in 1833. Under the guidance of NY Senator Martin Van Buren (soon to be Jackson’s Secretary of State and then Vice President), the new Democratic Party expanded its base to include not only Southern slave owners but urban workers and immigrants in the North, Western and Northern small farmers. Van Buren also expanded the party system to include state and local branches that coordinated their actions with the national party. When Jackson first ran in 1824 and again in 1828, American men were voting for the president or the electors in the Electoral College. Jackson also worked to expand the amount of land that white farmers could own by forcibly removing Native tribes from the southeast part of the country and relocating them west of the Mississippi River.
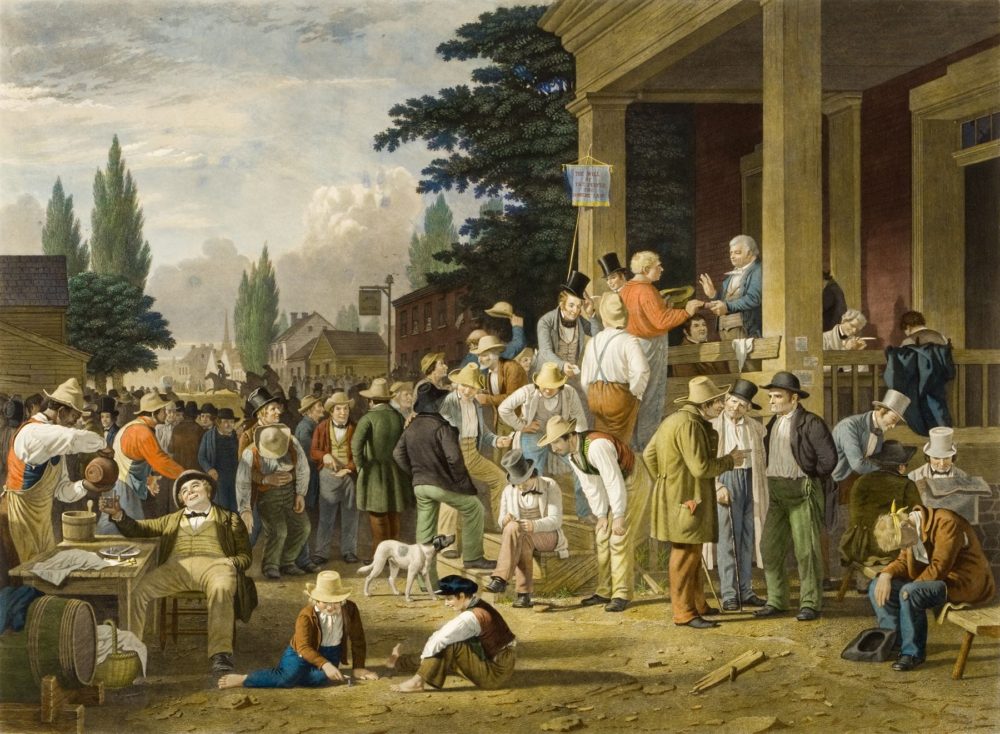

Eligibility for Federal Office and Choosing the Presidential Candidates
Under Jefferson, candidates were usually chosen based upon the ideal of a democratic republic – educated, usually wealthy landowners (and sometimes slaveowners). After taking office, Jefferson did not remove many government officials but did work with Congress to try to limit the power of the federal courts (remember Adams’ midnight judges during his lame duck time in 1801). During Jefferson’s time, the duty of an elected official was to vote on what he believed to be the best choice for the country and not vote primarily for regional interests. They feared that tyranny came from exercising the will of the majority over the minority (whether it be slave owners, small states, or the wealthy). This did change by the time Jackson became president in 1829. Also, during Jefferson’s time, each party’s Congressional leaders held a caucus during the election year and nominated their top candidate(s). This also changed under Jackson. Beginning in 1824 and starting a long standing tradition in 1828, the party’s national convention named the presidential nominee. As the right to vote expanded before and during Jackson’s tenure, almost any white male of voting age was seen as a proper candidate for office. More and more officials were decided by the voters including state and local judges, members of the electoral college, and state governors. Jackson removed dozens of government officials as well once he became president, viewing those offices as for and by the people and not ones that should be held exclusively by that office holder. Furthermore, under Jackson, he and other elected officials saw themselves as carrying out the will of the people while in office. Tyranny, in Jackson’s time, was seen as elected officials ignoring the will of the people and imposing their own values and views on issues. Jackson believed that the people could “arrive at right conclusions” and “instruct their… representatives” accordingly.
Role of Federal Government in Promoting the Economy
Jefferson initially fought Hamilton’s Bank of the United States but eventually came to accept its existence. He also believed that manufacturing, commerce, and shipping were important, but, as mentioned before, the agrarian economy took precedence over those aspects of the economy. We see this in the purchase of the Louisiana Territory. We also see that during Jefferson’s presidency, he worked with Congress to lower the whiskey taxes and then eventually eliminate them. He also kept government spending under control, though this was done through his cooperation with a Republican-dominated Congress and not through vetoes of bills (Jefferson didn’t veto any bills during his presidency). However, Jefferson’s biggest knock against the economy was the devestating Embargo Act of 1807 that killed American exports, dropped agriculture prices, but ironically, spurred on domestic manufacturing to meet the needs of the American people.
Jackson, on the other hand, fought with the BUS and wielded the veto against it to kill it in 1832. He also weakened it by removing the deposits of government funds from the BUS between 1832-1836. This battle with the BUS and its eventual end, coupled with the Specie Circular and bad banking news from Britain sparked the worst depression in American history until 1893 (but that happened after his presidency). Of his other 11 vetoes, more than half of those stopped federal government spending on internal improvements around the country, which probably would have benefitted the American economy. Jackson believed in a limited federal government debt as well. So it appears that both men didn’t subscribe to pro-business policies and would eventually damage their country’s economic prospects.

The Exercise of Federal Power
As previously mentioned, Jefferson did not veto any bills during his two terms, but he did steer a course that he thought would protect American interests abroad. When the Barbary pirates continued to seize American shipping in the Mediterranean, Jefferson sent American warships and mediators to deal with this threat to American neutrality and commerce. Jefferson acted as a guide to Congress in order to get his policies passed. In the purchase of the Louisiana Territory, he moved away from his strict interpretation of the Constitution and took a more expansive or loose interpretation of his foreign affairs power. Additionally, enforcing the Embargo with the U.S. Navy contradicted the Republicans’ traditional view of the narrow use of federal power. Jefferson explained his abandonment of strict interpretation of the Constitution like this in 1810:
“…a strict observance of the written laws is doubtless one of the high duties of a good citizen: but it is not the highest. the laws of necessity, of self-preservation, of saving our country when in danger, are of higher obligation. to lose our country by a scrupulous adherence to written law, would be to lose the law itself, with life, liberty, property & all those who are enjoying them with us; thus absurdly sacrificing the end to the means.”
Jackson, on the other hand, believed in a limited federal government (Congress and the Courts) but an expansive and vigorous executive branch. Jackson ignored Supreme Court decisions at least twice (McCulloch, Worcester) and vetoed 12 bills from Congress, more than the previous six presidents combined. He was also a strong nationalist and during the tariff crisis with South Carolina, was ready to march on the state once they decided to nullify the tariff in 1833. Granted, Congress did give him authorization to do so with the Force Act, but even if they hadn’t, some historians agree that he likely would have gone to South Carolina and enforced the collection of the tariff anyway. He let the responsibility to defend the nation squarely on his shoulders. In addition, when abolitionists started mailing anti-slavery newspapers and other publications to Southern religious and political leaders in the South, Jackson initially asked Congress to pass a law to stop these mailings. When Congress refused, he ordered all American postmasters to remove anti-slavery material from the U.S. mail. Part of this expansive use of executive power came from Jackson’s view of the presidency as a “tribune” of the people who would do their will.
So, after having read these areas of similarity and difference, in your mind, who was the better democrat and why? Provide specific examples from the blog and your own notes and reading to support your assertion.

