Blog #151 – Final Exam – Debate Over Expansion
Before, during, and after the Spanish-American War in 1898, Americans had debated whether or not America should go beyond its borders and become an imperial empire, much like the European countries had done during the 19th Century w/ Asia and Africa. Below are the arguments for and against imperialism and some of its proponents and opponents.
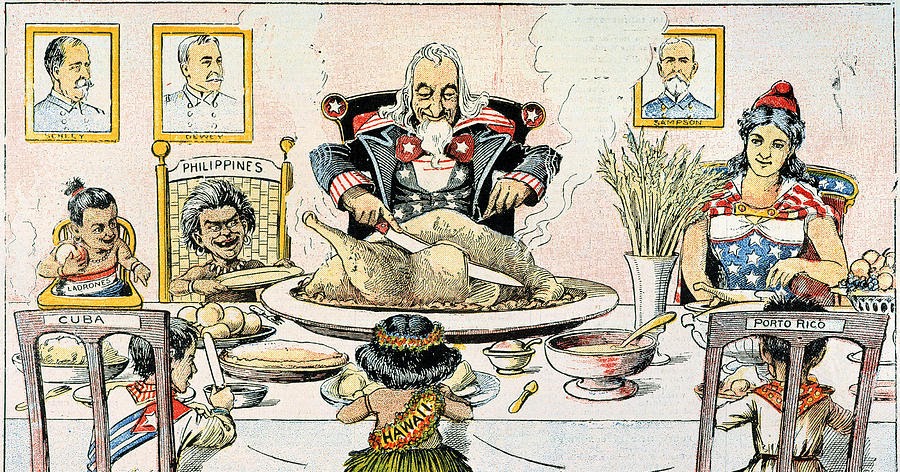
For Imperialism
People for it: Assistant Secretary of the Navy Teddy Roosevelt, Senator Henry Cabot Lodge, Alfred T. Mahan, President William McKinley, Judge William Howard Taft, Admiral George Dewey, Reverend Josiah Strong, former Secretary of State William Seward, and Senator Albert Beveridge.
Arguments for imperialism:
- To give back the Philippines to Spain would be cowardly and dishonorable.
- To let other imperial powers have the Philippines was bad business and discreditable.
- Granting the Filipinos their independence was irresponsible because they are unfit to rule themselves. They need America to civilize, uplift, and Christianize them.
- Imperialism is good for America. It invigorates a nation and keeps it healthy. A slothful nation will victim to those countries that maintain soldierly virtues.
- Annexation of the Philippines would put America into a position to dominate trade with China and the rest of Asia.
- We need the markets and raw materials now. It doesn’t matter that the Philippines are non-contiguous. We didn’t need the purchases and additional areas in the continental U.S., but look at us now! We produce more than we can consume.
- Annexation would be so easy because we already control the islands.
- Filipinos don’t have to become citizens of the U.S., we will treat them as dependents (like we do with the Native Americans). The 14th Amendment won’t apply to them.
- Republicans favored annexation because it made the party look good after winning the war.
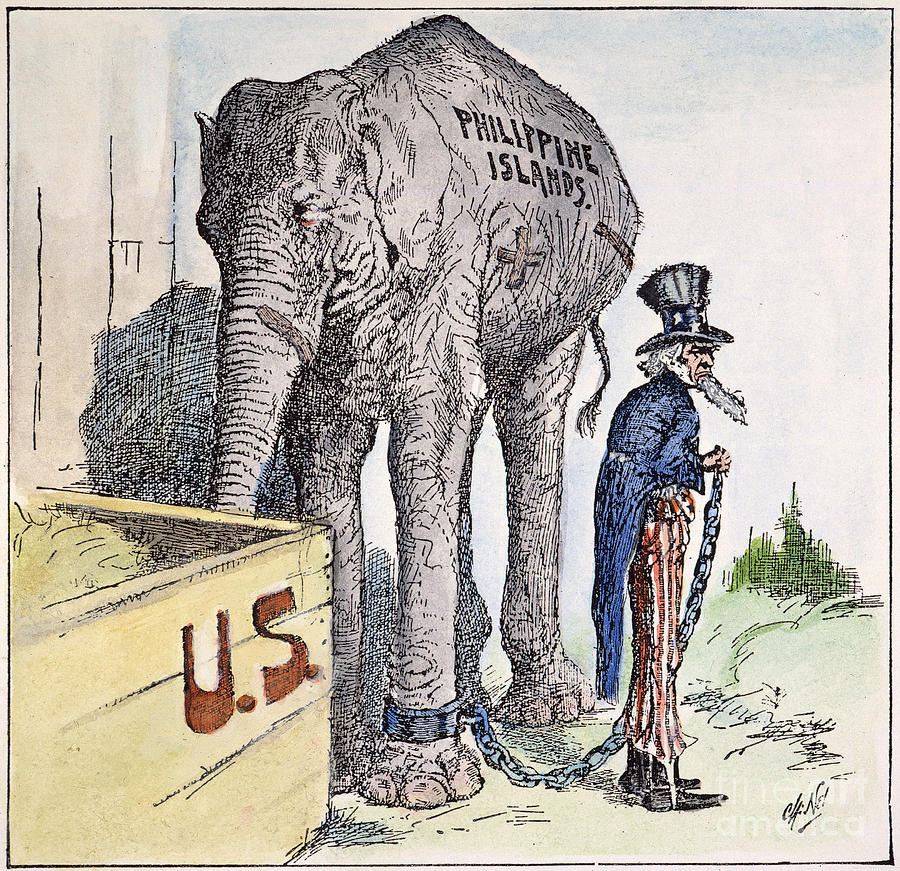
Against Imperialism
People against it: Author Mark Twain, former president Grover Cleveland, Speaker of the House Thomas “Czar” Reed, journalist Lincoln Steffens, Jane Addams, former Democratic presidential candidate William Jennings Bryan, AFL chief Samuel Gompers, industrialist Andrew Carnegie, Harvard professor William James.
Arguments against imperialism
- Imperialism is immoral. It repudiates our commitment to human freedom and liberty. We instead think we know what is best for the Filipinos, and that is wrong.
- Nativists fear the pollution of the white American population with inferior Asian races, especially when they are allowed to move to the U.S. Acquisition of the Philippines may require that they become citizens.
- Industrial workers feared the flood of additional cheap labor which would further undercut job opportunities.
- Imperialism puts us in the international stage of world politics and is a constant menace for war. War carries off the physically and mentally fit and leaves behind the lesser fit. It threatens our security, internally and externally.
- The “civilizing” mission some claim is really a cover for a desire to loot the colonies and their natural resources. This misson is self-righteous and pretentious.
- We will inherit Spain’s task of suppressing the native peoples when they rebel. They will NOT want our cultural ways. We will end up like Spain – a shriveling power.
- Can’t we just trade without having to annex other territories?
- Imperialism would involve the need for a large standing army which would become a heavy tax burden.
The country chose imperialism, and the Senate voted narrowly for the Treaty of Paris, 1898, 57 to 27, one more vote needed for the 2/3 approval.
Your job:
Pretend you are a senator back in 1898. Pick a region of the country and a party (both parties were for expansion, especially Southern Democrats). Feel free to write from the POV of the Senator and give a speech either advocating expansion or opposing it, or just explain which arguments hold more sway with your Senator and why? Explain.
Here is some info on the 1898 U.S. Senate elections. Maybe choose your senator from someone who ran and look up his views on the war. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1898_and_1899_United_States_Senate_elections










 In 2000, Naomi Klein published a book called No Logo that examined the pervasive marketing of brands and how companies like Nike, Starbucks and others were reinventing themselves as companies who didn’t make stuff anymore but marketing ideas. Nike could outsource the making of its shoes and become “the idea of transcendence through sports” while Starbucks was the “idea of community” (Klein). After listening to Howard Schulz’s biography Forward on CD, (CEO of Starbucks), I can tell you that concept is EXACTLY what they’ve been trying to sell for the past decade.
In 2000, Naomi Klein published a book called No Logo that examined the pervasive marketing of brands and how companies like Nike, Starbucks and others were reinventing themselves as companies who didn’t make stuff anymore but marketing ideas. Nike could outsource the making of its shoes and become “the idea of transcendence through sports” while Starbucks was the “idea of community” (Klein). After listening to Howard Schulz’s biography Forward on CD, (CEO of Starbucks), I can tell you that concept is EXACTLY what they’ve been trying to sell for the past decade.






